GlasSense II
2016 - 2017
Research project
Published on JoVE
Featured on JoVE Monthly Highlights : Feb. 2018
본 연구는 음식 섭취를 포함한 다양한 육체 활동을 안경 형태의 웨어러블 디바이스로 감지하고 머신 러닝을 통해 분류하는 GlasSense의 설계부터 제작, 평가까지 일련의 과정을 소개한다. 연구에 소개된 방법을 통해 저작, 윙크, 휴식, 말하기, 걷기 활동을 91.4%의 F1 점수로 분류할 수 있다.
[Abstract]
This study presents a series of protocols of designing and manufacturing a glasses-type wearable device that detects the patterns of temporalis muscle activities during food intake and other physical activities. We fabricated a 3D-printed frame of the glasses and a load cell-integrated printed circuit board (PCB) module inserted in both hinges of the frame. The module was used to acquire the force signals, and transmit them wirelessly. These procedures provide the system with higher mobility, which can be evaluated in practical wearing conditions such as walking and waggling. A performance of the classification is also evaluated by distinguishing the patterns of food intake from those physical activities. A series of algorithms were used to preprocess the signals, generate feature vectors, and recognize the patterns of several featured activities (chewing and winking), and other physical activities (sedentary rest, talking, and walking). The results showed that the average F1 score of the classification among the featured activities was 91.4%. We believe this approach can be potentially useful for automatic and objective monitoring of ingestive behaviors with higher accuracy as practical means to treat ingestive problems.
Contribution
Co-author of Design and Evaluation of Smart Glasses for Food Intake and Physical Activity Classification, a JoVE article.
- 3D Modeling & fabrication of glasses-type wearable device (100%)
Tools & Skills
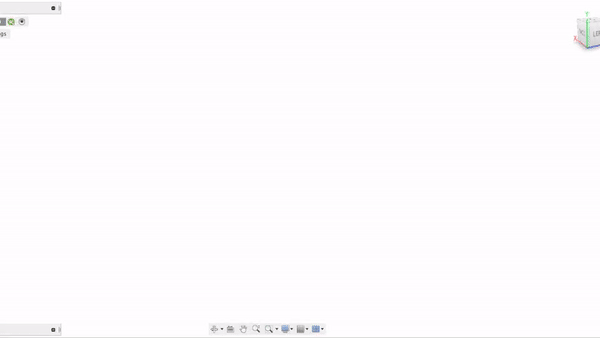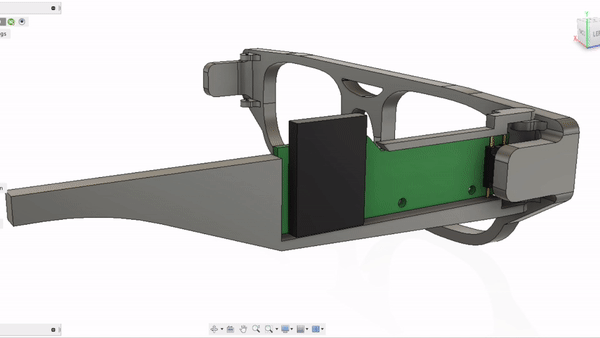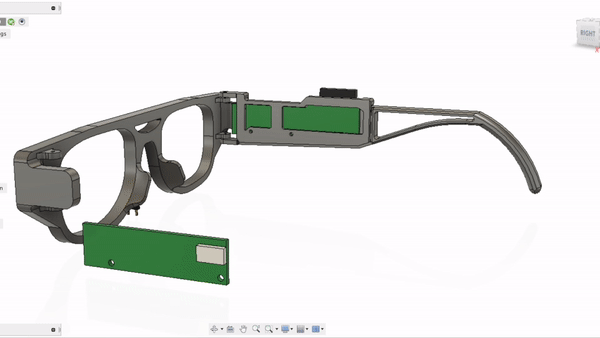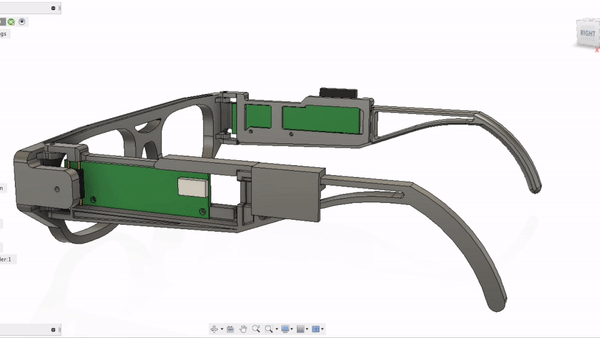
GlasSense II is self-contained not only with load cells but with two PCBs including MCU, Wi-Fi module, and battery. Design was conducted under the following requirements.
1. Every component must be 3d-printable.
2. Ergonomics and mass distribution must be taken into consideration, since it will actually be worn by test subjects.
3. Must include calibration element for responding to face shape difference among test subjects.